
Marathi and English Medium
मानवी वस्ती व भूमी उपयोजन या वरील दिर्घोत्तरी प्रश्न
Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail
मानवी वस्ती व भूमी उपयोजन या वरील दिर्घोत्तरी प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1) आकृतीबंधानुसार वस्त्यांचे मुख्य प्रकार स्पष्ट करा.
उत्त्तर- मानव हा समाजशील प्राणी असल्याने तो नेहमी समूहाने राहणे पंसत करतो. यातूनच पुढे सामाजिक बांधिलकी व सामाजिक गरजार्माण होत असतात. या सामाजिक गरजेतून अनेक लोक एखादया ठिकाणी एकत्रित येऊन विशिष्ट पध्दतीने घरे बांधतात, अशा घरांच्या मांडणीला वस्ती असे म्हणतात.
वस्त्यांच्या आकार आणि प्रकार यांत भिन्नता आढळते त्या एका खेडयापासुन ते महानगरांपर्यत्न असु शकतात.
आकृतीबंधानुसार वस्त्यांचे प्रकार-
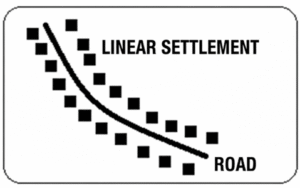
1) रेषीय वस्ती – एखाद्या रस्त्यालगत, रेल्वेलाईन, नदी, कालव्याला लागून रेषीय वस्त्या तयार होतात. रेषीय वस्त्या रेषेत असतात किंवा रस्त्याच्या अथवा नदीच्या आकाराप्रमाणे रेषेत समांतर पसरत जातात
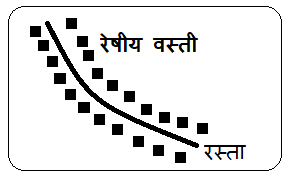
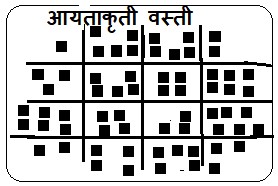
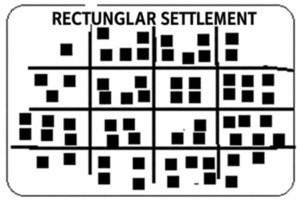
2) आयताकृती वस्ती– आयताकृती वस्तीत घरे ओळीत किंवा सरळ रेषेत असतात आयताकृती वस्तीतील रस्ते ओळीत व एकमेकांना समांतर असतात आधुनिक काळात नियोजित शहरे वसवतांना अशा आकाराचा विचार केला जातो
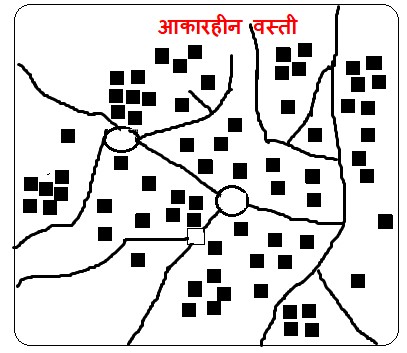
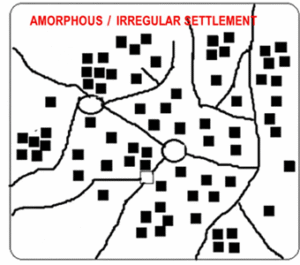
3) आकारहीन वस्ती– वस्तींच्या निर्मितीनंतर वस्तींच्या चालणाऱ्या अनेक कार्यांबरोबर व त्या कार्याच्या विकासाबरोबर अशा वस्तीचा आकार वाढत जातो. वस्ती वाढतांना अनियमित आकाराने वाढत जाते, या वस्ती प्रकारात सोयीनुसार आणि जागेच्या उपलब्धतेनुसार घरे बांधलेली असतात.
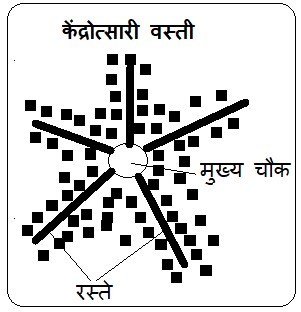
4) केंद्रोत्सारी वस्ती– या वस्ती प्रकारात वस्तीतील एखाद्या केंद्राच्या भोवती वस्त्यांचा विकास झालेला असतो हा केंद्रबिंदू वस्त्यांच्या विकासातील महत्त्वपूर्ण भाग असतो
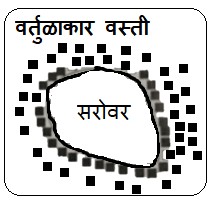
5) वर्तुळाकार वस्ती– एखाद्या तळ्याच्या विहिरीच्या किंवा सरोवराच्या आजूबाजूला अशा प्रकारच्या वस्त्या आकार घेतात पाण्याच्या उपलब्धतेमुळे घरे जवळजवळ व गोलाकार बांधली गेलेली असतात
6) त्रिकोणी वस्ती- दोन नद्यांच्या किंवा रस्त्यांच्या संगमावर किंवा समुद्राकाठी अशा प्रकारच्या त्रिकोणी आकाराच्या वस्त्या निर्माण होतात प्राकृतिक

किंवा सामाजिक कारणांमुळे अशा वस्त्यांची वाढ तिन्ही बाजूंनी होते नदी
मानवी वस्ती व भूमी उपयोजन या वरील दिर्घोत्तरी प्रश्न
Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail
प्रश्न- 2) ग्रामिण भूमी उपयोजन स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तर-
# ज्या ठिकाणच्या वस्तीची लोकसंख्या 5000 पेक्षा कमी असते व तेथील लोकसंख्येची घनता दर चौ. कि. मी.ला 400 पेक्षा कमी असते व तेथील जास्तीत जास्त लोक प्राथमिक व्यवसायात गुंतलेले असता अशा वस्तीस ग्रामीण वस्ती असे म्हणतात.”
# मानवाने भूमीचा केलला उपयोग म्हणजे भूमी उपयोजन होय. उदा. घरे, रस्ते, धरणे, दवाखाने, विविध कार्यालये बांधण्यासाठी जमीनीचा केलेला उपयोग म्हणजे भूमी उपयोजन होईल.
ग्रामीण भूमी उपयोजन-
① वन – ग्रामिण भागातील वनांचे क्षेत्र हे ग्रामीण भूमीउपयोजनात येते. ग्रामिण भागात हे क्षेत्र मोठया प्रमाणावर आढळते.
② बिगरशेती – ग्रामिण भागात असलेल्या पायाभूत सोयी, उद्योग, दुकाने, इत्यादींचा समावेश या वर्गात होतो. व्दितीयक व तृतीय व्यवसायांच्या विकासामुळे दिवसेंदिवस या भूमी उपयोजनात वाढ होत आहे.
③ ओसाड (नापीक) व अनुत्पादक भूमी :
जी भूमी कृषी व्यवसायाखाली कोणत्याही प्रकारचे तंत्र वापरून आणता येत नाही अशी भूमी या प्रकारात येते.
उदा. उंचसखल डोंगराळ भूमी, ओसाड वाळवंट, घळीयुक्त भूमी इ.
④ कायमस्वरूपी गायरान व चराऊ जमीन-
ही जमीन प्रामुख्याने ग्रामपंचायतीच्या किंवा शासनाच्या मालकीची असते. अशी जमीन फारच थोड्याप्रमाणात खाजगी मालकीची असू शकते. या जमीनातुन ग्रामपंचयात सर्वाजनिक मिळकत मिळवू शकते.
⑤ किरकोळ वृक्ष, पिके व वनराई, जमीन-
ग्रामीण भागातील फळबागा व फळझाडांखालील क्षेत्राचा यात समावेश होतो. भूमी उपयोजनाच्या या प्रकारात निव्वळ लागवडीखालील क्षेत्र येत नाही. या प्रकारातील अशा जमिनी खाजगी मालकीच्या असतात.
⑥ पिकाऊ अनुत्पादक जमीन- जमीनीच्या या प्रकारात जमीन पाच वर्षांपेक्षा अधिक काळ पडीक (पडीत) असते. ही जमीन कोणत्याही वेळेस भर घालून, तिची गुणवत्ता वाढवून लागवडीखाली आणता येते.
⑦ चालू पडजमीन – एक वर्ष किंवा त्यापेक्षा कमी काळ लागवडीखाली नसलेली जमीन या क्षेत्रात येते. काही वेळा जास्त उत्पन्न मिळविण्याच्या उद्देशाने जमिनीला जाणीवपूर्वक पड ठेवण्याच्या शेती शास्त्रिय विचारातुन चालू पडजमीन निर्मीती होत असते. या काळात जमीन नैसर्गिकरीत्या पुन्हा कसदार बनते .
⑧ चालू पडशिवायची पड जमीन–
जमीनीचा हा प्रकारसुध्दा लागवडी योग्य जमीनीचाच असतो. जी जमीन एक वर्षापेक्षा जास्त पंरतु पाच वर्षां पेक्षा कमी काळ पडीक राहते, ती या प्रकारात मोडते.
⑨ निव्वळ लागवडीखालील क्षेत्र:
प्रत्यक्ष लागवड केलेले व ज्यातून उत्पादन घेतलेले आहे असे शेती खालील क्षेत्र म्हणजे निव्वळ लागवडीखालील क्षेत्र होय.
Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail
प्रश्न 3 ) नागरी भूमी उपयोजनाचे सविस्तर विवेचन करा.
① निवासी क्षेत्र : नागरी भागातील माणसाने स्वतःच्या निवासासाठी बांधकाम केलेले क्षेत्र म्हणजे निवासी क्षेत्र होय.
उदा. रहीवास परीसर, सोसायटया, रो- हाऊस, रो- बंगलो
② औद्योगिक क्षेत्र : अशी जमीन, जेथे कोणत्या न कोणत्या वस्तु निर्मितीचे कार्य चालते, जेथे लोक स्वतःच्या उपजीविकेसाठी काम करतात.
③ संस्थात्मक क्षेत्र – शैक्षणिक संस्था, विद्यापीठे, मुख्य कार्यालये, छावणी इत्यादींच्या कार्यासाठी व्यापलेली जमीन. या जमिनीचा वापर वरील कार्यांसाठी केला जातो.
④ मनोरंजनाखालील क्षेत्र: नागरिकांच्या मनोरंजनाची साधने उपलब्ध असलेली जमीन, जेथे नागरिक मनोरंजन किंवा करमणुकीसाठी जातात. उदा. खेळाचे मैदान, बाग, सिनेमागृह, नाट्यगृह इ.
⑤ वाहतूक : या जागेचा वापर एका ठिकाणाहून दुसऱ्या ठिकाणी जाण्यासाठी होतो. यामध्ये विमानतळ, रेल्वेस्थानक, रस्ते, नैसर्गिक बंदर, लोहमार्ग इत्यादींचा समावेश होतो.
⑥ व्यापारी क्षेत्र : नागरी क्षेत्र, ज्या जमिनीवर पक्क्या मालाची दैनंदिन विक्री होत असते असे क्षेत्र. अनेक ठिकाणी हे क्षेत्र निवासी क्षेत्रातही आढळते. काही ठिकाणी मात्र असे क्षेत्र विविध प्रकारचा माल मिळण्याच्या दृष्टीने एका ठिकाणी केंद्रित झालेले आढळतात. उदा. केंद्रीय व्यापारी क्षेत्रे.
⑦ रेखांकित/सीमांकित भूखंड : हे मोकळे भूखंड असतात. ज्याचा वापर इमारतीच्या बांधकामासाठी केला जातो. हे क्षेत्र प्रामुख्याने नागरी क्षेत्राच्या सीमेवर आढळते. वाढत्या लोकसंख्येच्या दबावामुळे कृषीखालील जमिनीवर या क्षेत्राचे अतिक्रमण होते.
⑧ संमिश्र भूमी उपयोजन – एखादया क्षेत्रात विभिन्न प्रकारचे भूमी उपयोजन एकत्रित पाहावयास मिळते. निवासी, व्यावसायिक, औद्योगिक या प्रकारचे भूमी उपयोजन एकाच क्षेत्रात एकत्रितपणे आढळून येते. अशा क्षेत्रांमध्ये घरे, व्यवसाय, दुकाने, शाळा, दवाखाने मोकळ्या जागा एकाच ठिकाणी असु शकतात.
Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail
मानवी वस्ती व भूमी उपयोजन या वरील दिर्घोत्तरी प्रश्न
Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail
प्रश्न 4 ) कार्यानुसार नागरी वस्तीचे प्रकार –
उत्तर- काही शहरे विशिष्ट कार्यासाठी, विशिष्ट क्रियांसाठी, उत्पादनासाठी, सेवांसाठी ओळखली जातात. नगराच्या प्रमुख कार्यानुसार शहरांची नगरांचे पुढील प्रकारे वर्गीकरण केले जाते.
① प्रशासकीय नगरे-
या शहरामध्ये राज्याची राजधानी, उपराजधानी व जिल्ह्याच्या मध्यवर्ती कार्यालयाच्या ठिकाणांचा समावेश होतो.
उदा. तालुक्याचे शहर चाळीसगाव, जिल्ह्याचे शहर- जळगाव राज्याच्या राजधान्या – मुंबई, गांधीनगर, पटणा
② औद्योगिक शहरे –
• अशा शहरात कारखानदारी हे कार्य महत्वाचे असते. काही शहरात निरनिराळ्या उद्योगांचा समावेश होतो. औदयागीक शहरात उद्योगावर आधारित इतर पूरक उद्योग व व्यवसाय देखिल स्थापन झालेले असतात.
उदा. मुंबई, ठाणे, पुणे, पटणा, जामनगर, लंडन इ.
③ वाहतूक नगरे –
वाहतूक मार्गाच्या केंद्रीकरणामुळे अशा प्रकारची नगरे निर्माण होतात.
उदा. मुंबई, पुणे, मनमाड, भुसावळ शिकागो, पॅरीस, टोकियो, कैरो इ.
④ व्यापारी शहरे-
अशी शहरे कच्च्यामालाच्या उत्पादक प्रदेशात निर्माण झालेली असतात.
उदा. मुंबई, कोल्हापुर, सुरत, इंदौर लंडन इ.
⑤ खाणकाम शहरे –
ज्या वस्तीत कोणत्या ना कोणत्या खनिजाचे उत्खन्नन होत असते, अशा वस्त्या खाणकाम शहरे म्हणून उदयास येतात. खनिजे बाहेर काढणे, त्यावर प्रक्रिया करणे, त्यांची वाहतूक करणे, इ. या प्रकारची कार्य या ठिकाणी चालतात.
उदा. गडचिरोली, भंडारा, अंकलेश्वर जोहान्सबर्ग इ.
⑥ शैक्षणिक नगरे –
काही शहरांमध्ये विद्यापीठे, विज्ञान तंत्रज्ञान, महाविद्यालये अशा विविध संस्थांचे केंद्रीकरण झालेले असते. अशा शहरांचा शैक्षिणिक शहरे असे म्हणतात. शैक्षणिक शहरे ही सांस्कृतिक कार्याचा वारसा चालवितात.
उदा. पुणे, वाराणसी, नालंदा ऑक्सपर्ड, केंब्रीज
⑦ धार्मिक शहरे –
काही ठिकाणांना धार्मिक गोष्टींमुळे महत्त्व प्राप्त होते. श्रध्देमुळै अशा ठिकाणांना लोक भेटी देतात यातुन धार्मिक शहरांची निर्मीती होते त्यांच्या कार्यात वाढ / विकास होतो.
उदा. शिर्डी, पंढरपुर, वाराणसी, मक्का-मदीना इ. शहरे.
⑧ पर्यटन शहरे –
जगात ऐतिहासिक, धार्मिक व सांस्कृतिक तसेच निसर्ग सौदर्य असणारी ठिकाणे ही पर्यटन केंद्रे म्हणून नावारूपाला आली आहेत. थंड हवेची ठिकाणे अशा ठिकाणांना हौशी पर्यटक भेटी देतात त्यातुन या नगरांच्या कार्यात वाढ होते व नगरांचा विकास होतो.
उदा. महाबळेश्वर, गणपतीपुळे, गोवा, शिमला, बॅडेन, बॉलिवुड
अधिक वाचा-
मानवी वस्ती व भूमी उपयोजन – कारणे द्या
मानवी वस्ती व भूमी उपयोजन वस्तूनिष्ठ प्रश्न
Download PDF of All Text Books

English Medium
Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail
मानवी वस्ती व भूमी उपयोजन या वरील दिर्घोत्तरी प्रश्न
Long Answer Question / Descriptive Question
Q.1) Explain the main types of settlements according to their patterns.
Answer:
Since human beings are social animals, they prefer to live in groups. This leads to the development of social bonds and social needs. Due to these social needs, many people come together at a place and build houses in a specific manner. Such an arrangement of houses is called a settlement.
Settlements differ in size and type. They may range from a small village to a metropolitan city.
Types of settlements according to pattern:
1) Linear Settlement:
Linear settlements develop along roads, railway lines, rivers, or canals. The houses are arranged in a straight line or extend parallel to the shape of the road or river.
2) Rectangular Settlement:
In a rectangular settlement, houses are built in rows or straight lines. The roads are straight and parallel to each other. In modern times, such a pattern is considered while developing planned cities.
3) Irregular Settlement:
After the formation of a settlement, as various activities continue and develop, the settlement gradually expands. During this growth, it spreads in an irregular manner. In this type, houses are constructed according to convenience and availability of space.
4) Radial (Centrifugal) Settlement:
In this type of settlement, development takes place around a central point. This central point plays an important role in the growth and development of the settlement.
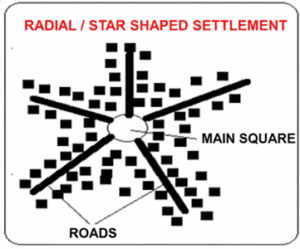
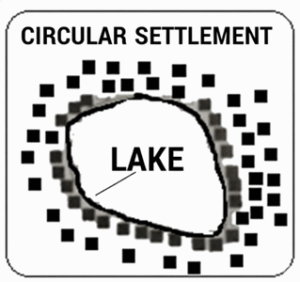
5) Circular Settlement:
Such settlements develop around a pond, well, or lake. Due to the availability of water, houses are built close to each other in a circular shape.
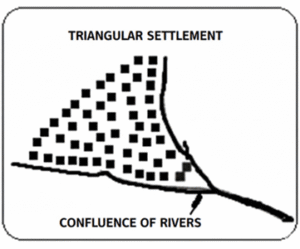
6) Triangular Settlement:
Triangular settlements develop at the confluence of two rivers or roads, or along the seashore. Due to natural or social factors, such settlements expand on all three sides.
Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail
Q.2) Explain rural land use.
Answer:
A settlement with a population of less than 5,000, population density of less than 400 persons per sq. km, and where the majority of people are engaged in primary occupations is called a rural settlement.
The use of land by humans is called land use. For example, the use of land for building houses, roads, dams, hospitals, and various offices is termed land use.
Rural Land Use:
1) Forest:
Forest areas in rural regions are included under rural land use. Such areas are found on a large scale in rural regions.
2) Non-agricultural Land:
This includes land used for infrastructure facilities, industries, shops, etc., in rural areas. Due to the growth of secondary and tertiary occupations, this type of land use is increasing day by day.
3) Barren (Waste) and Unproductive Land:
Land which cannot be brought under cultivation using any type of technology falls under this category.
Examples: rugged mountainous land, barren deserts, ravine lands, etc.
4) Permanent Pastures and Grazing Land:
This land is mainly owned by the Gram Panchayat or the government. Only a very small portion may be privately owned. The Gram Panchayat can earn public revenue from such land.
5) Land under Miscellaneous Trees, Crops, and Groves:
This includes areas under orchards and fruit trees in rural regions. Net sown area is not included in this category. Such land is usually privately owned.
6) Cultivable Waste Land:
In this type, land remains fallow for more than five years. With investment and improvement in quality, this land can be brought under cultivation.
7) Current Fallow Land:
Land that is not under cultivation for one year or less falls under this category. Sometimes, land is deliberately kept fallow for agricultural reasons to obtain higher yields. During this period, the soil naturally regains its fertility.
8) Other than Current Fallow Land:
This type is also cultivable land. Land that remains fallow for more than one year but less than five years is included in this category.
9) Net Sown Area:
The area actually cultivated and from which production is obtained is known as the net sown area.
Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail
Q.3) Types of Urban Settlements According to Functions
Answer:
Some cities are known for specific functions, activities, production, or services. Based on the main function of a town or city, urban settlements are classified as follows:
1) Administrative Cities
These cities include state capitals, sub-capitals, and district headquarters where major administrative offices are located.
Examples: Taluka town – Chalisgaon; District town – Jalgaon; State capitals – Mumbai, Gandhinagar, Patna
2) Industrial Cities
In such cities, industrial activity is the most important function. Various industries are established, along with supporting and ancillary industries and occupations.
Examples: Mumbai, Thane, Pune, Patna, Jamnagar, London
3) Transport Cities
These cities develop due to the concentration and junction of transport routes.
Examples: Mumbai, Pune, Manmad, Bhusawal, Chicago, Paris, Tokyo, Cairo
4) Commercial Cities
Such cities develop in regions producing raw materials and act as major centers of trade and commerce.
Examples: Mumbai, Kolhapur, Surat, Indore, London
5) Mining Cities
Settlements where the extraction of minerals takes place develop as mining cities. Activities such as extraction, processing, and transportation of minerals are carried out here.
Examples: Gadchiroli, Bhandara, Ankleshwar, Johannesburg
6) Educational Cities
Some cities have a concentration of universities, colleges, and institutions of science and technology. These are known as educational cities. They also preserve and promote cultural traditions.
Examples: Pune, Varanasi, Nalanda, Oxford, Cambridge
7) Religious Cities
Certain places gain importance due to religious beliefs. Devotees visit these places out of faith, leading to the development of religious cities.
Examples: Shirdi, Pandharpur, Varanasi, Mecca–Medina
8) Tourist Cities
Places with historical, religious, cultural importance or natural beauty develop as tourist centers. Hill stations and scenic locations attract tourists, which enhances urban functions and leads to city development.
Examples: Mahabaleshwar, Ganpatipule, Goa, Shimla, Baden, Bollywood


[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
छान विश्लेषण
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]
[…] Human Settlements and Land Use Answer in Detail […]